Overview
The DevOps Starter Project simplifies the setup of an entire continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) pipeline to Azure with Azure DevOps. You can start with existing code or use one of the provided sample applications. Then you can quickly deploy that application to various Azure services such as Virtual Machines, App Service, Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS), Azure SQL Database and Azure Service Fabric.
DevOps Projects does all the work for the initial configuration of a DevOps pipeline including everything from setting up the initial Git repository, configuring the CI/CD pipeline, creating an Application Insights resource for monitoring, and providing a single view of the entire solution with the creation of a DevOps Projects dashboard in the Azure portal.
What’s covered in this lab?
In this lab, you will
- Create an ASP.NET sample DevOps project using DevOps Starter feature in Azure
- Examine the CI/CD pipelines configured by DevOps Starter
- Commit the code changes and execute CI/CD
- Configure Azure Application Insights monitoring
Pre-requisites for the lab
-
Microsoft Azure Account: You will need a valid and active Azure account for the Azure labs. If you do not have one, you can sign up for a free trial
-
If you are a Visual Studio Active Subscriber, you are entitled for a $50-$150 credit per month. You can refer to this link to find out more including how to activate and start using your monthly Azure credit.
-
If you are not a Visual Studio Subscriber, you can sign up for the FREE Visual Studio Dev Essentialsprogram to create Azure free account (includes 1 year of free services, $200 for 1st month).
-
-
You will need an Azure DevOps account. If you do not have one, you can sign up for free here.
Exercise 1: Setting up a sample ASP.NET project using DevOps Starter Project
-
Sign into the Microsoft Azure portal.
-
In the search box, type DevOps , and then select DevOps Starter. Then click on Create DevOps Starter

-
By default DevOps Starter project setup with GitHub. Click on change settings here to change the destination to Azure DevOps and click Done
-
Now select the .NET sample application and click Next.
-
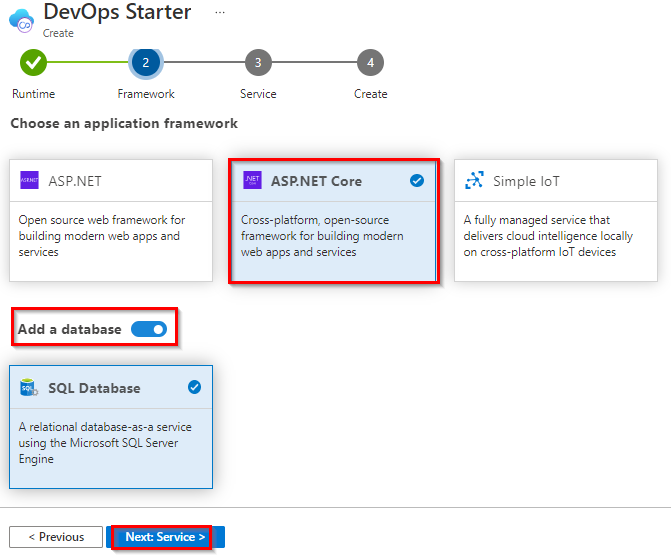
The .NET samples include a choice of either the open source ASP.NET framework or the cross-platform .NET Core framework. Select the .NET Core application framework. This sample is an ASP.NET Core MVC application. And also enable Add a database toggle to add the database to the application. When you’re done, choose Next.
-
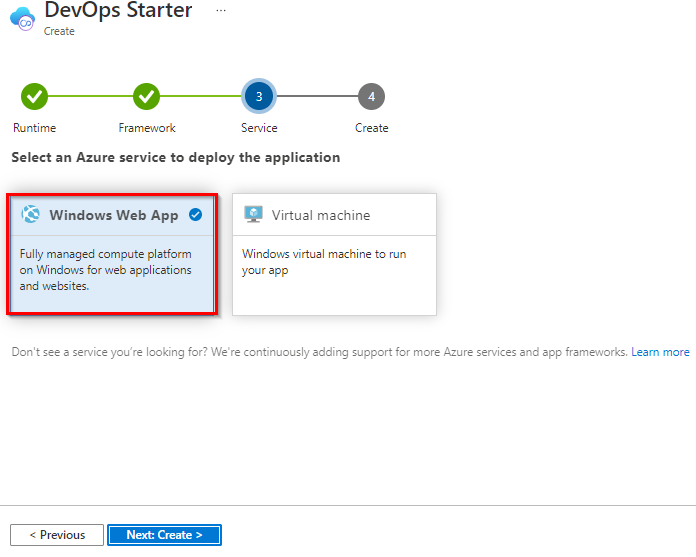
Web App on Windows is the default deployment target. You can optionally choose Virtual Machine also. When you’re done, choose Next.
-
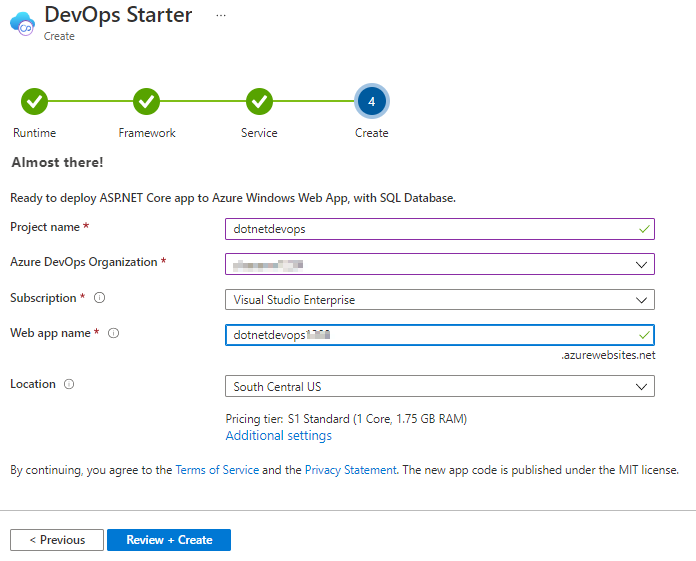
Select your Azure DevOps organization and choose a name for your project and Web app. When you’re done, choose Review + Create.
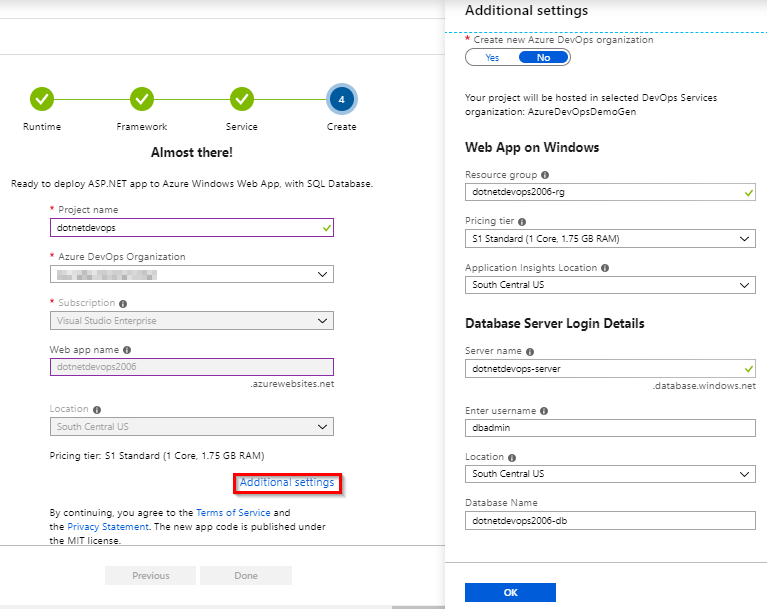
You can click on Additional Settings if you would like to edit web app and database parameters
-
Once the deployment completes, click Go to resource.
-
DevOps project dashboard loads as shown in below image.
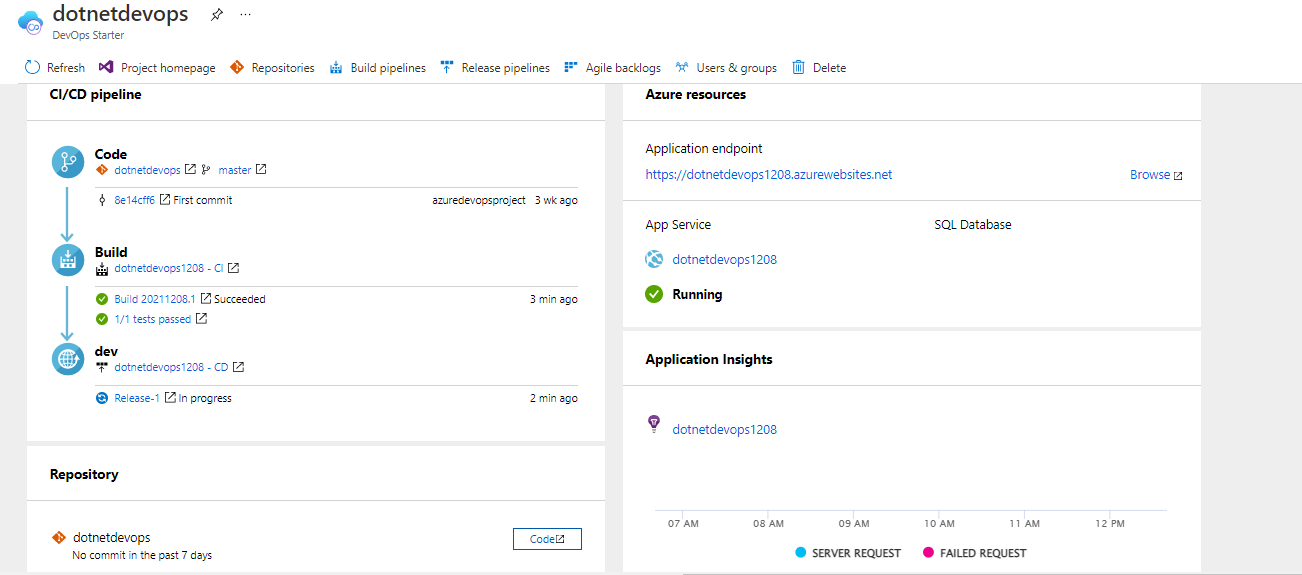
DevOps project
-
Created a team project with sample .NET code repository
-
Created a build and release pipelines to compile, test and deploy the application
-
Created Azure Web App and Azure SQL database in Azure using Azure Pipelines
If Azure Resources are not created, they will be created by CI/CD pipeline. You can track pipeline status in ‘CI/CD pipeline’ section
You’re now ready to collaborate with a team on an ASP.NET Core app with a CI/CD process that automatically deploys your latest work to your web site.
-
-
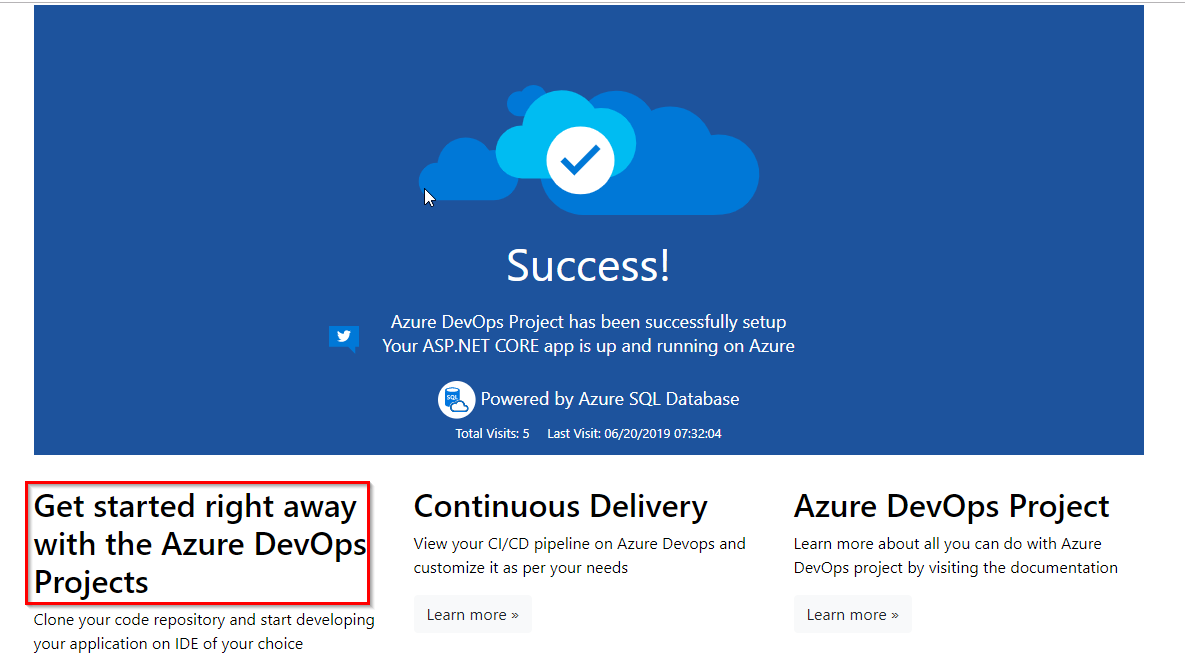
On the right side of the dashboard, select Browse to view your running application.
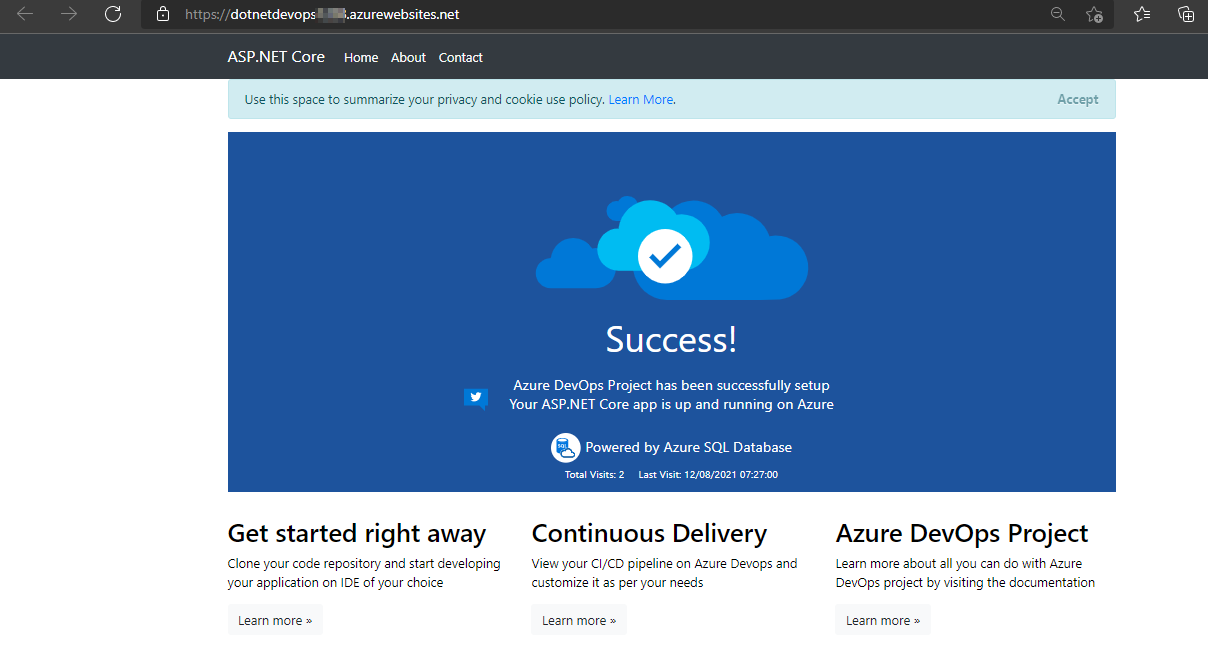
The web app looks like as shown in the below figure
Exercise 2: Examine the CI/CD pipelines configured by Azure DevOps Project
The Azure DevOps Starter project automatically configured a full CI/CD pipeline in your Azure DevOps organization. You can explore and customize the pipeline as needed. Follow the steps below to familiarize yourself with the Azure DevOps build and release pipelines.
-
Select Build Pipelines from the top of the Azure DevOps project dashboard. This link opens a browser tab and the Azure DevOps build pipeline for your new project.
-
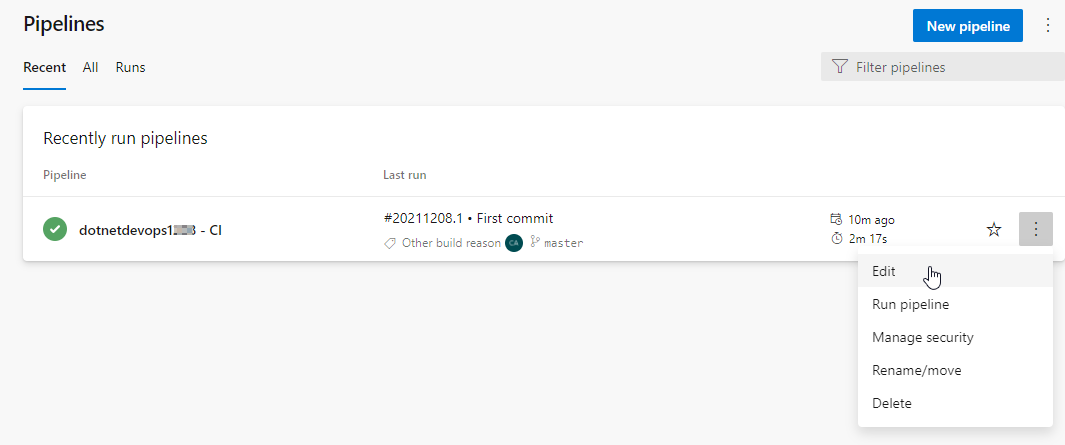
Select Edit.
-
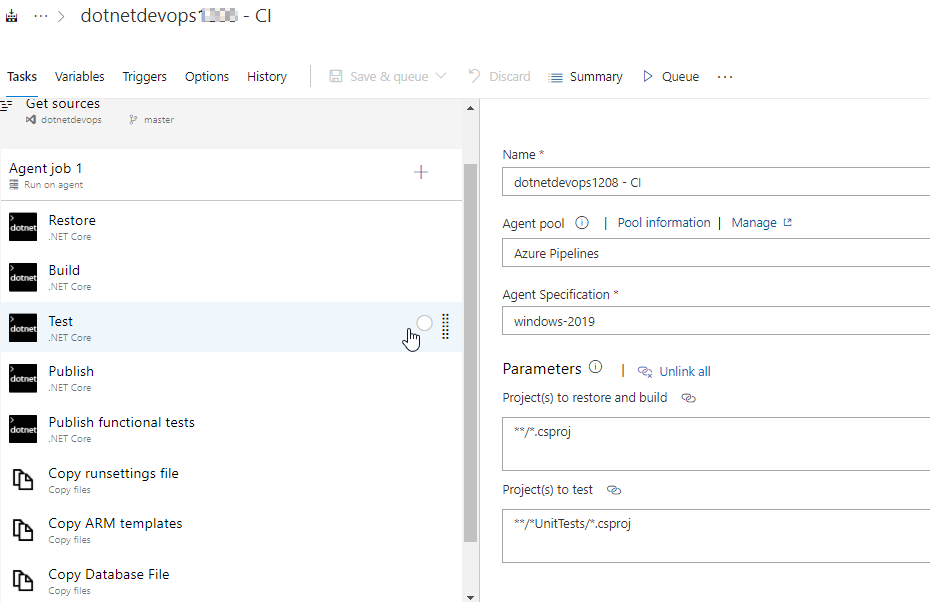
In this pane, you can examine the various tasks for your build pipeline. This build pipeline performs various tasks such as fetching sources from the Git repository, restoring dependencies, compile the application, run tests and publishing outputs used for deployments.
-
Under your build pipeline name, select History. You see an audit trail of your recent changes for the build. Azure DevOps keeps track of any changes made to the build definition and allows you to compare versions.
-
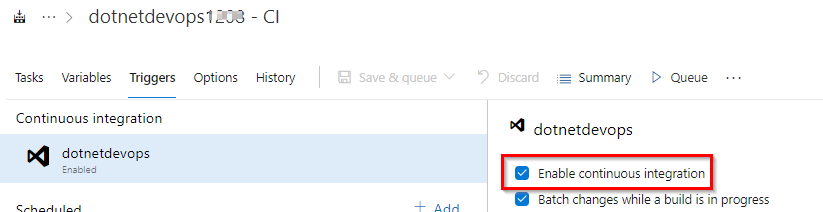
Select Triggers. The Azure DevOps project automatically created a CI trigger and every commit to the repository initiates a new build. You can optionally choose to include or exclude branches from the CI process.
-
Select Releases under Pipelines section.
The Azure DevOps project created a release pipeline to manage deployments to Azure.
-
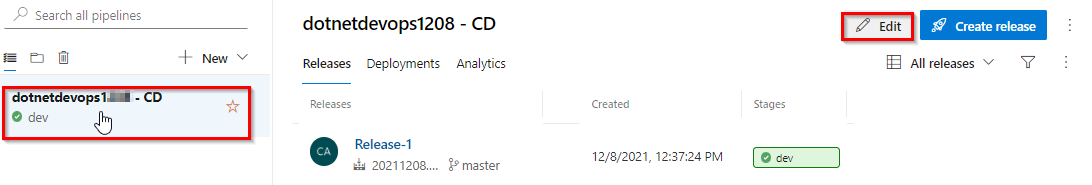
Select the release pipeline, then choose Edit.
-
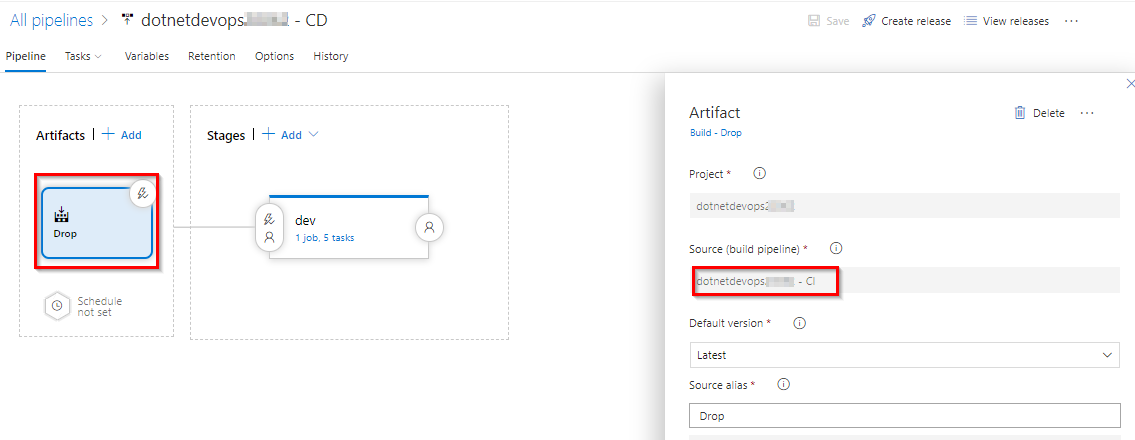
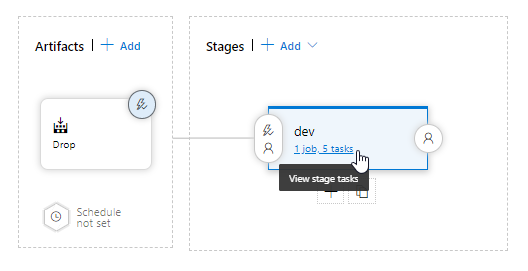
Under Artifacts, select Drop. The build pipeline you examined in the previous steps produces the output used for the artifact.
-
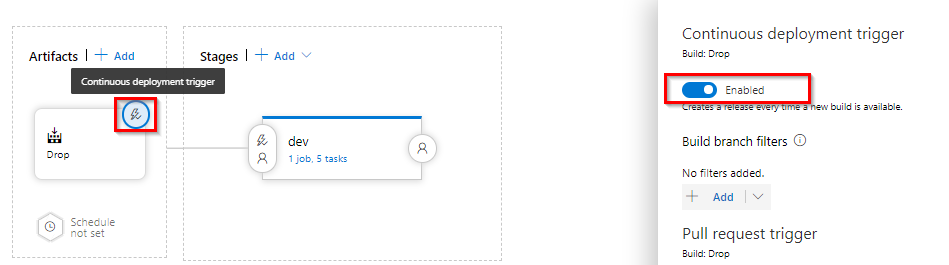
To the right-hand side of the Drop icon, select the Continuous deployment trigger. This release pipeline has an enabled CD trigger, which executes a deployment every time there is a new build artifact available. Optionally, you can disable the trigger, when your deployments require manual execution.
-
Select Tasks. The tasks are the activities your deployment process performs. In this example, you have five tasks.
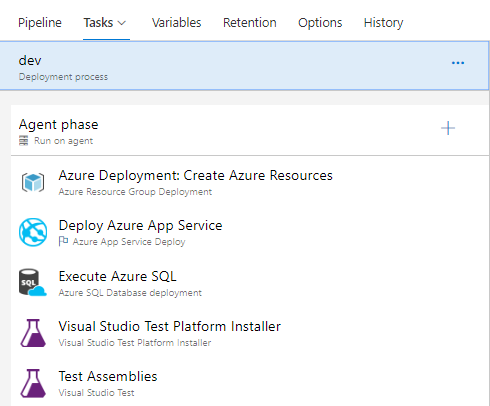
- Azure Resource Group Deployment task deploy the required Azure resources, Azure Web app and Azure SQL database for the application to use.
- Azure App Service Deploy task deploy the application package to the web site
- Azure SQL Database deployment task deploy SQL changes to the database.
- Visual Studio Test tasks run functional tests after the successful deployment of the application
-
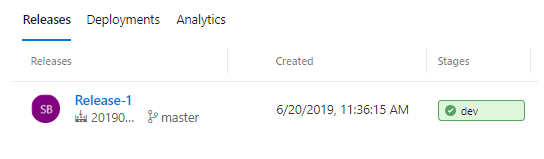
On the right-hand side of the browser, select View releases. This view shows a history of releases.
-
Click on the release number to view the release summary. There are several menus to explore from this view such as a release summary, associated work items, and tests.
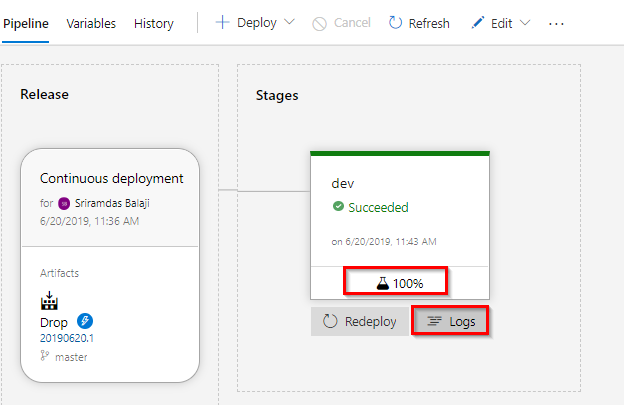
-
Select Logs. The logs contain useful information about the deployment process. They can be viewed both during and after deployments.
Exercise 3: Commit the code changes and execute CI/CD
The Azure DevOps project created a Git repository in your Azure DevOps organization. Follow the steps below to view the repository and make code changes to your application.
-
Select Repos to view the created Git repository by Azure DevOps project.
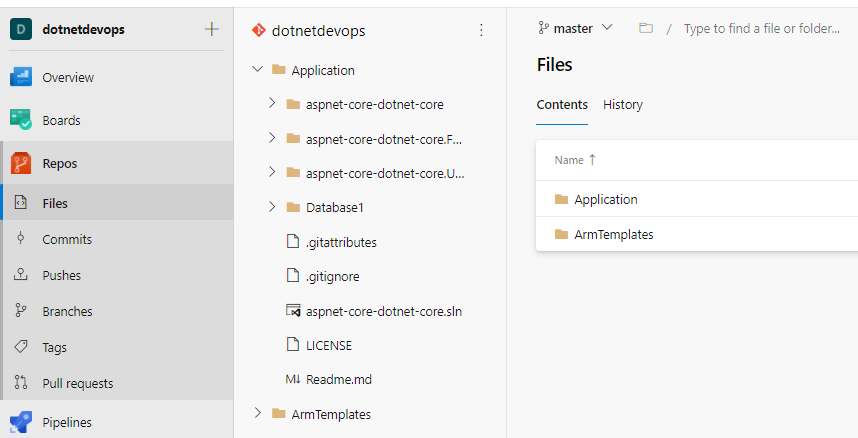
-
To view the repository clone URL, select Clone from the top right of the browser. You can clone your Git repository in your favourite IDE. In this lab, you can use the web browser to make and commit code changes directly to the master branch.
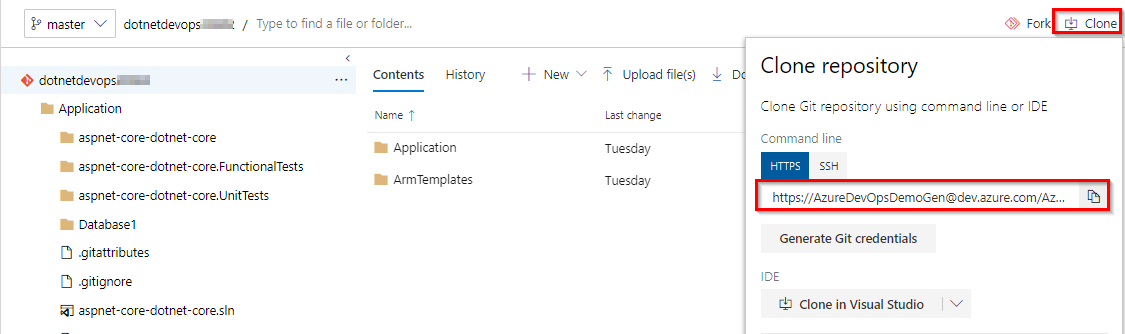
-
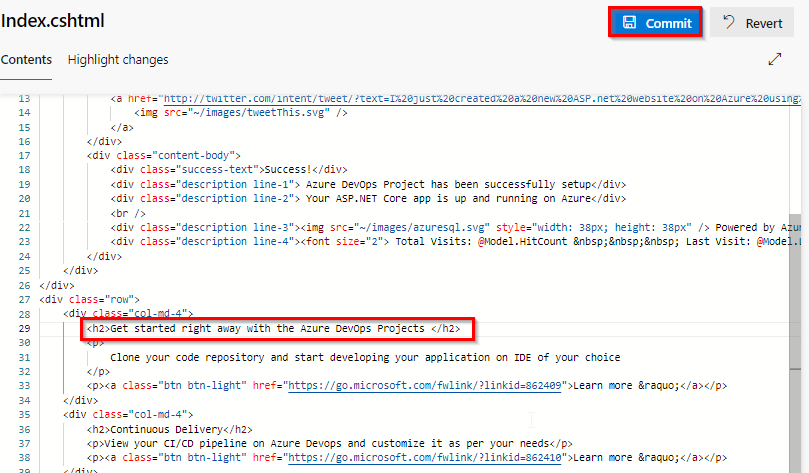
On the left-hand side of the browser, navigate to the Application/aspnet-core-dotnet-core/Pages/Index.cshtml file. Select Edit, and make a change.
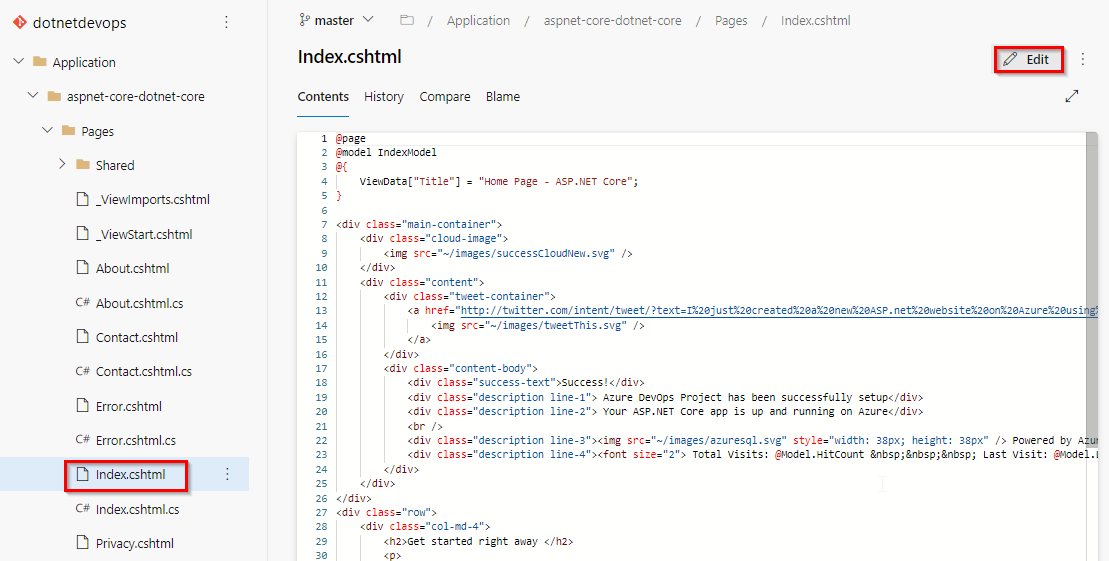
Make a change to the h2 heading. For example, type Get started right away with the Azure DevOps Projects or make some other change. Choose Commit, to save and check-in your changes.
-
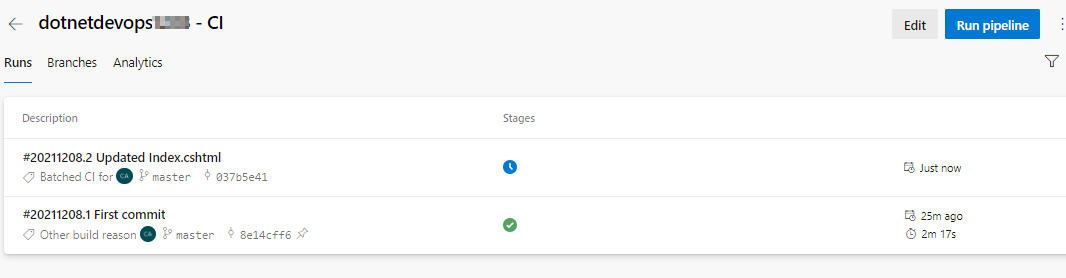
In your browser, navigate to the Pipelines | Pipelines. You should now see a build is in progress. The changes you just made are automatically built and deployed via Azure DevOps CI/CD pipelines.
-
Once the Build and Release are completed in your browser, navigate to the Azure DevOps project dashboard. On the right side of the dashboard, select Browse to view your updated running application. You will see the updated header in the web app.